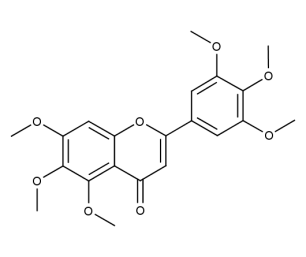
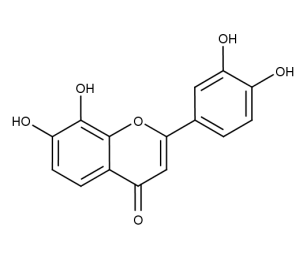
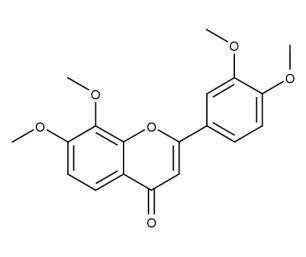
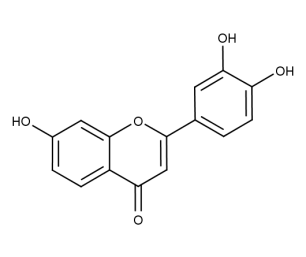
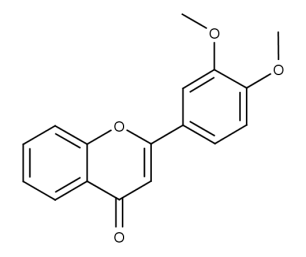
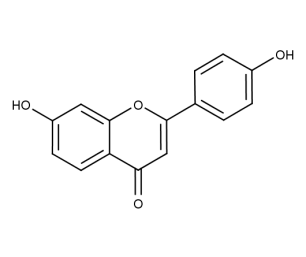
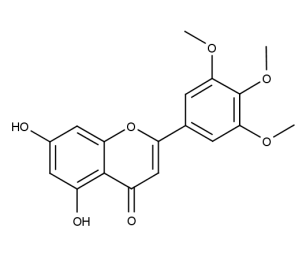
- Code : #1187 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₃
- CAS : 19725-47-4
Flavone
Flavones are a subclass of flavonoids, polyphenolic compounds found in various plants, fruits, vegetables, and herbs. They play a crucial role in protecting plants from pathogens and ultraviolet radiation. Chemically, flavones are characterized by a basic structure consisting of two aromatic rings connected by a pyran heterocycle. Major dietary sources of flavones include parsley, celery, chamomile, and certain citrus fruits. Flavones have attracted scientific interest due to their numerous biological properties. They are particularly known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities. Studies have shown that flavones can inhibit lipid oxidation, thereby neutralizing free radicals responsible for cellular aging and various chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, flavones modulate certain cellular signaling pathways involved in the proliferation of cancer cells. Most common substances are derivatives of Apigenin and Luteolin. We offer a large range of such glucosylated, hydroxylated or methylated analytical standards. Traditional medicinal plants like dandelion, sage, mint and ginkgo biloba are rich in luteolin. These plants have been used historically in various cultures for their therapeutic properties, some of which may be linked to their luteolin content.
- Code : #1269 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₂O₈
- CAS : 29043-07-0
- Code : #1307 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₆
- CAS : 3440-24-2
- Code : #1308 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₉H₁₈O₆
- CAS : 65548-55-2
- Code : #1223 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₅
- CAS : 2150-11-0
- Code : #1204 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₄
- CAS : 4143-64-0
- Code : #1297 5 mg
- Formula : C₁₇H₁₄O₄
- CAS : 4143-62-8
- Code : #1259 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₄
- CAS : 2196-14-7
- Code : #1106 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₁₈H₁₆O₇
- CAS : 18103-42-9
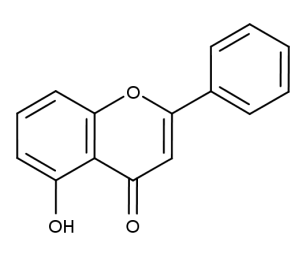
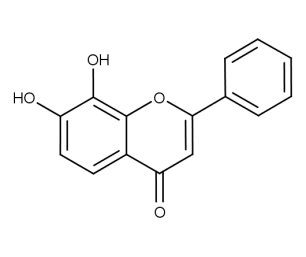
- Code : #1019 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₃
- CAS : 491-78-1
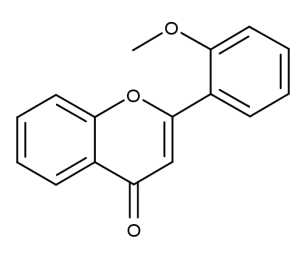
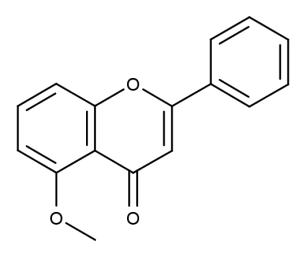
- Code : #1020 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₃
- CAS : 42079-78-7
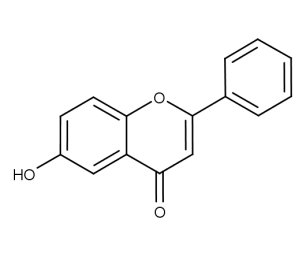
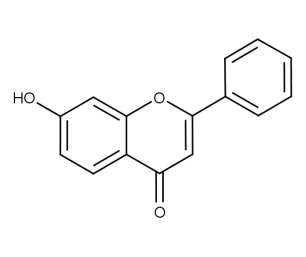
- Code : #1059 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₃
- CAS : 6665-83-4
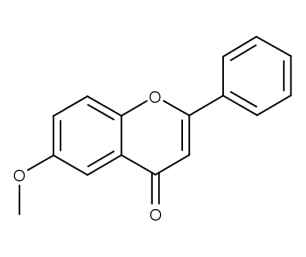
- Code : #1062 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₃
- CAS : 26964-24-9
- Code : #1013 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₄
- CAS : 38183-03-8
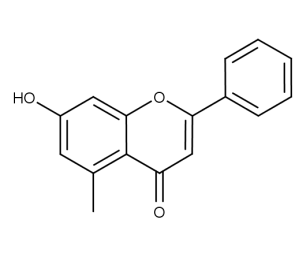
- Code : #1149 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₃
- CAS : 15235-99-1
- Code : #1060 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₃
- CAS : 6665-86-7