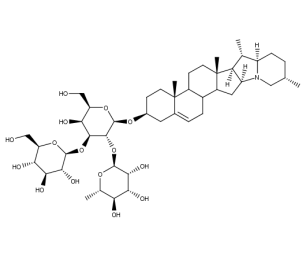
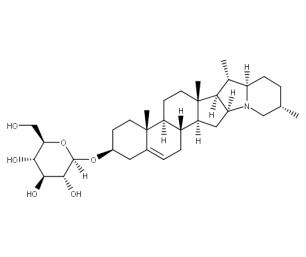
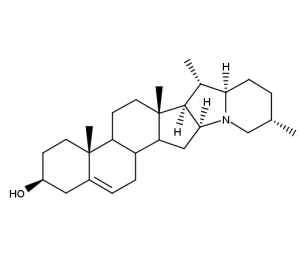
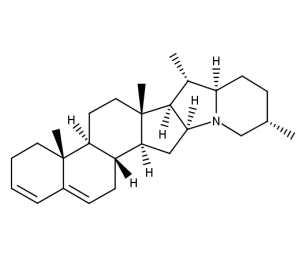
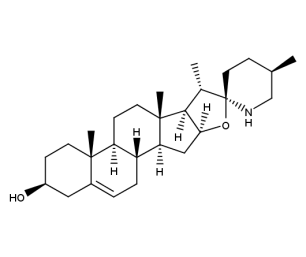
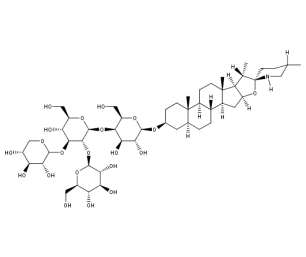
- Code : #1553 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₅H₇₃NO₁₄
- CAS : 20562-03-2
Glycoalkaloid
Glycoalkaloids are a class of naturally occurring compounds found in plants, particularly in the Solanaceae family, which includes potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers. They are secondary metabolites produced by the plants as a defense mechanism against herbivores and pathogens. Glycoalkaloids are composed of a sugar molecule (glyco-) and an alkaloid molecule (-alkaloid), which is issued from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. The most common glycoalkaloids found in potato tubers are solanine and chaconine, which can be toxic to humans if ingested in large quantities. Tomatine is specific to tomato. Glycoalkaloids have been studied for their potential health benefits, including anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties, but their consumption should be monitored and limited to safe levels.

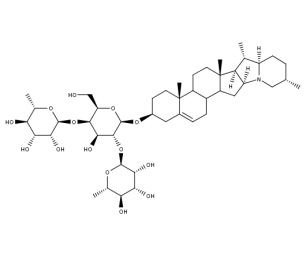
- Code : #1653 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₅H₇₃NO₁₅
- CAS : 20311-51-7
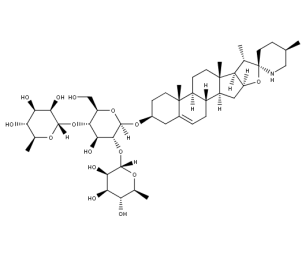
- Code : #1652 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₅H₇₃NO₁₅
- CAS : 20562-02-1
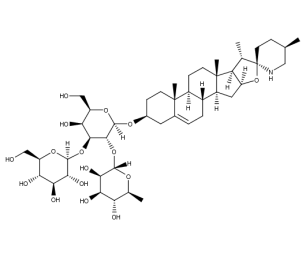
- Code : #1658 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₅H₇₃NO₁₆
- CAS : 19121-58-5
- Code : #1554 5 mg
- Formula : C₃₃H₅₃NO₆
- CAS : 511-36-4
- Code : #0681 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₄₃NO
- CAS : 80-78-4
- Code : #1654 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₄₁N
- CAS : 26516-51-8
- Code : #1655 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₄₃NO₂
- CAS : 126-17-0
- Code : #0684 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₄₅NO₂
- CAS : 77-59-8
- Code : #0602 100 mg
- Formula : C₅₀H₈₃NO₂₁
- CAS : 17406-45-0